
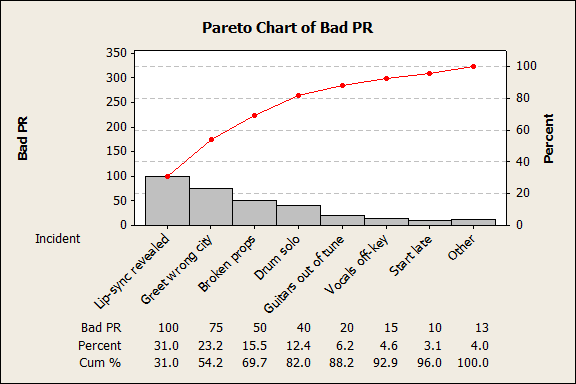
How do we know which is the response and independent variable? It depicts the link between a process component on one axis and the quality fault on the other to help with process optimization.Ī scatter diagram demonstrates the relationship between a change in a dependent variable Y in response to a change in a corresponding independent variable X. What is a scatter diagram?Ī scatter diagram is a graph that shows the association between two variables for a collection of numerical data. At first glance, this may be confusing, but scatter diagrams are easy to understand if you take the time. While typical charts and graphs use lines or bars to represent data, scatter diagrams use dots. They are simple to use and help in improving business processes. Scatter diagrams are graphical statistical tools. It is used to plan and monitor operations to improve quality-related issues in an organization. They can be an aid in identifying the best use of limited resources by identifying the most significant variables warranting intervention.A scatter diagram is one of seven core tools in project management. Pareto charts identify the most frequent process factors. As a result, they can reveal relationships between variables. They describe process characteristics over time. This is a basic SPC tool that conveys the average or mean of the data, the variation present, variation patterns, and whether or not the process is within specifications. These are also known as herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams or Ishikawa diagrams, Fishbone diagrams are best for problem-solving, as they can illustrate the relationships between different variables. There are a number of control charts that may be used for SPC.

Control charts also make it possible to distinguish between normal variations and those warranting investigation. Variations within the process over time stand out clearly within this context. This chart illustrates the statistical stability of a particular process.

Control – SPC control charts, performance managementįrom the efforts detailed above, the generated data is then plotted on a control chart.Improve – modeling, tolerance control, defect control, design changes.Analyze – Fishbone diagrams, failure analysis, root cause analysis.Measure – defect metrics, data collection, sampling.Define – benchmarking, process flow mapping, flowcharts.Common activities during these stages can include: This acronym represents the stages Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control. SPC follows a set process known as DMAIC. As a result, the information is easily read, greatly simplifying the task of monitoring and acting upon the information. Data is plotted within the confines of specific zones and rules to represent these contextual factors accurately. For example, factors such as shifts, operators and production events would be included in an SPC study within a lean manufacturing Six Sigma program. Within Statistical Process Control, data is statistically compared within the context of its occurrence. SPC applies statistical methods to achieve this task. While a host of tools and measures are typically used within a lean Six Sigma program, one in particular, Statistical Process Control or SPC, examines processes as well as identifying sources of variation. Isolating the cause of such variations greatly simplifies effectively re-defining processes, enabling organizations to perform and produce in an improved manner. Using Statistical Process Control to Identify VariationĪ robust system of metrics is significant not just to analyze progress during a lean Six Sigma transformation, but can aid in identifying the source of variation and waste.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
